Are Drying Cabinets Energy-Efficient?
Introduction
A drying cabinet is an electrical appliance used to dry items such as clothing, equipment, or other textiles that should not be machine dried. Drying cabinets use heated air circulation to expedite the drying process, providing an efficient alternative to line drying or room drying wet gear and clothing.
With rising energy costs, many wonder if drying cabinets are an energy efficient option compared to other drying methods. On one hand, drying cabinets use electricity to power fans and heaters. But on the other hand, they can dry items more quickly and thoroughly than passive drying. This raises the question: Are drying cabinets an energy efficient option for drying clothing and equipment?
How Drying Cabinets Work
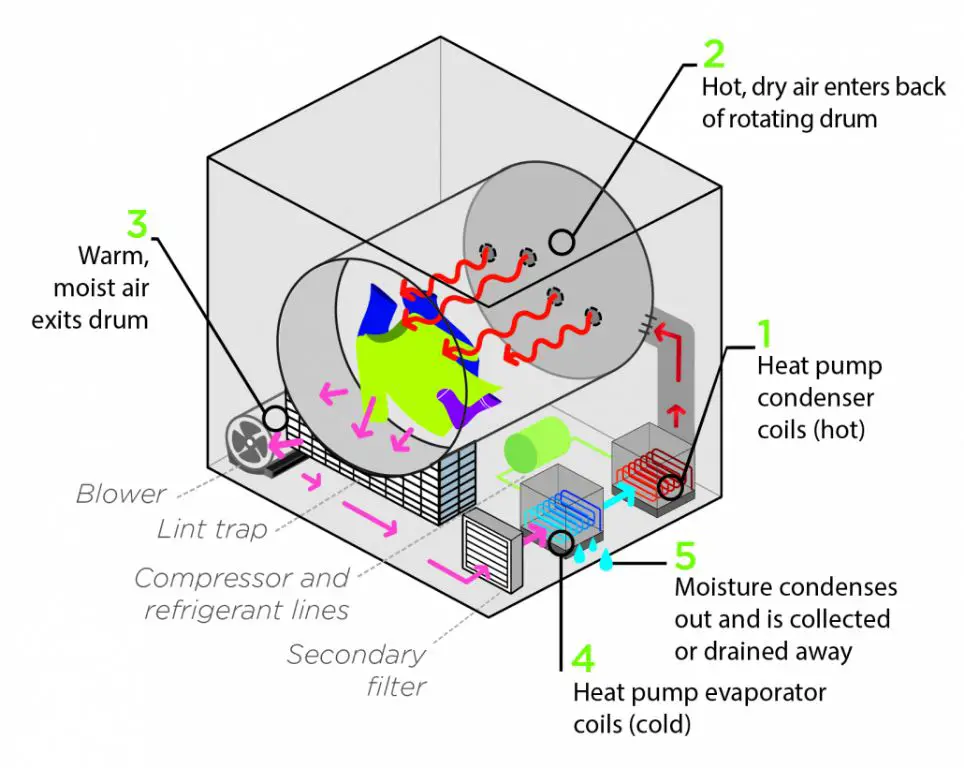
Drying cabinets utilize heated air to dry items like clothing, shoes, and other textiles. They work similarly to a conventional clothes dryer, but on a larger scale with adjustable racks. According to Wikipedia, a drying cabinet is “an electrical machine designed to expedite the drying of items – usually clothing – that are unsuitable for a mechanical tumble dryer.”
The main components of a drying cabinet are a metal cabinet, adjustable shelves/hanging rods, heating element, fan, humidity sensor, and control panel. The cabinets are insulated to retain heat. Clothes or other items are placed inside on shelves or hangers. The user selects the desired drying temperature and time on the control panel.
When started, a heating element heats the air inside the cabinet to a preset temperature, typically between 80-140°F. The fan circulates the hot air around the cabinet to dry the items. A humidity sensor monitors moisture levels and shuts off the heating element when the desired dryness is achieved. Temperature, time, and humidity settings can be adjusted based on the fabric type and drying needs.
Drying cabinets provide gentle, even drying for delicate items not suitable for machine tumble drying. The process dries items faster than air drying and uses less energy than a clothes dryer.
Energy Use of Drying Cabinets
Drying cabinets use significantly less electricity compared to conventional clothes dryers. The power consumption of a typical drying cabinet ranges from 50-150 watts, which translates to 0.05 to 0.15 kW/h (kilowatt hours) [1]. In comparison, an electric clothes dryer can use anywhere from 1800 to 5000 watts, or 1.8 to 5 kW/h [2].
On average, a drying cabinet running 6 hours per day for 30 days will consume between 27-81 kW/h per month. This is roughly equivalent to running a 60W light bulb continuously for a month. In contrast, an electric clothes dryer used twice per week could easily consume 200-300 kW/h per month [3].
So while drying cabinets do consume electricity, their energy usage is significantly lower than conventional dryers. Their efficient design and use of technologies like heat pumps allow them to effectively dry items while using a fraction of the energy.
Energy Efficiency Features
Modern drying cabinets utilize several design features that improve energy efficiency compared to older models. One key advancement is the use of heat pump technology, which recirculates hot air and removes moisture more efficiently than a standard heating element. For example, ASKO states their new heat pump drying cabinets have a low energy consumption but a high drying efficiency.
Insulation is another important factor. Drying cabinets with thick insulation around the walls and door help retain heat and prevent energy waste. Some models also have a reversible door, allowing the door hinge to be switched based on the cabinet’s placement to prevent heat loss when opened.
Advanced moisture sensors precisely detect the dryness level and automatically shut off when the laundry reaches the desired dryness. This prevents over-drying which wastes energy. Digital controls allow users to select optimal settings like low heat or quick dry cycles to improve efficiency.
According to Nimo Verken, modern drying cabinets can be up to 95% more energy efficient than older models. Companies continuously improve designs to maximize efficiency.
Drying Cabinet vs. Clothes Dryer
Drying cabinets are generally much more energy efficient than traditional tumble clothes dryers. According to Nimo (source), drying cabinets use only about 25% of the energy of a conventional tumble dryer to dry the same load of laundry. This significant energy savings is because drying cabinets rely on warm circulating air rather than intense heat to dry clothes. Additionally, the insulation in drying cabinets retains heat efficiently so less energy is required over time.
Tumble dryers must constantly generate high heat from electrical heating elements or gas burners to rapidly dry clothes. This requires much more energy input. According to Weekand (source), some drying cabinets include sensors to optimize drying time and further reduce energy use compared to tumble dryers which lack smart controls.
So for homeowners concerned about energy costs and efficiency, a drying cabinet is clearly the better option over a conventional tumble clothes dryer.
Cost Savings
Using a drying cabinet can provide significant cost savings compared to using a traditional clothes dryer. According to research by XDry, the average cost savings per year from using a drying cabinet instead of an electric clothes dryer is $2,433.31 (https://xdry.com/technical-data/cost-savings/).
This is calculated based on the average cost of electricity to run a clothes dryer ($0.15 per kWh) and the average yearly drying loads (416 loads per year). A standard electric clothes dryer uses about 3.3 kWh of electricity per load. In contrast, a drying cabinet like those from XDry only uses 1.5 kWh per average load.
At an average electric dryer cost of $0.50 per load ($0.15 x 3.3kWh), compared to $0.23 per load for a drying cabinet ($0.15 x 1.5kWh), the yearly savings amounts to $416 x ($0.50 – $0.23) = $2,433.31. So by using a drying cabinet instead of a traditional dryer, most households can save well over $2,000 per year on electricity costs alone.
The upfront cost of a drying cabinet ranges from $1,000 – $1,500. But with the electrical and maintenance savings, a drying cabinet can pay for itself in less than a year. This makes it a very cost-effective appliance compared to a traditional clothes dryer.
Environmental Impact
Drying cabinets have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional electric or gas clothes dryers. According to research from a 2023 study*, drying cabinets can reduce the carbon footprint of drying laundry by up to 65% compared to conventional tumble dryers. This drastic reduction in emissions is largely due to drying cabinets’ energy efficiency and lack of venting hot exhaust outdoors.
Modern drying cabinets utilize heat pump technology and recirculate air rather than venting it outside. This closed loop system retains heat and allows drying cabinets to operate using much less energy. Conventional tumble dryers lose heat through venting and require more energy to constantly heat replenished air. The study found that high efficiency drying cabinets like the Eco Dryer use just 0.05 kWh per kg of laundry dried. Older drying cabinets were found to use 0.37 kWh/kg, while conventional tumble dryers used up to 0.6 kWh/kg.
With significantly lower energy consumption, drying cabinets have a much smaller carbon footprint. If an average household in the U.S. used a drying cabinet instead of a conventional tumble dryer over one year, it would reduce CO2 emissions by 265 kg. This substantial reduction in emissions demonstrates the environmental benefits of the modern high efficiency drying cabinet.
* https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/16/3/1523
Proper Use for Efficiency
To operate a drying cabinet efficiently and maximize energy savings, follow these tips:
Fill the cabinet completely before running it. The more items inside, the more efficient the drying process since the cabinet won’t need to work as hard or as long to dry a full load 1.
Don’t overdry items. Remove clothes and fabrics as soon as they are dry to the touch to avoid wasting energy. The cabinet will continue drying items inside even after they are fully dry 2.
Clean the lint filter regularly to allow proper air circulation for efficient drying. A clogged filter will prolong drying times 3.
Allow adequate ventilation and spacing around the cabinet for air intake and exhaust.
Use the appropriate drying cycle and temperature for the fabrics being dried. Higher heat speeds drying but uses more energy.
Utilize moisture sensor technology to automatically shut off when items are dry.
Close the door securely to prevent loss of heated air.
Clean the condenser regularly if the unit recirculates air.
New Advancements
In recent years, drying cabinet technology has advanced considerably to improve energy efficiency. Many new models now utilize heat pump technology, which recirculates hot air and removes moisture to dry laundry efficiently using much less energy.
For example, Asko’s new heat pump drying cabinets have a dewatering capacity of 22 g/min, meaning they can dry a 4 kg load in just over 2 hours while using only 0.47 kWh of energy (Source: https://www.asko.com/za/laundry/drying-cabinets/drying-cabinets-features). This is a significant improvement compared to older drying cabinet models.
Nimo has developed a new drying cabinet line that is 95% more efficient than models produced 20 years ago. While old cabinets could use up to 6 kWh per cycle, Nimo’s new models average around 0.3 kWh (Source: https://www.nimoverken.com/en/landningssidor/modern-drying-cabinets-are-95-percent-more-energy-efficient-than-old_ones/).
Advancements like optimized air circulation, moisture sensors, and heat pumps have enabled drying cabinets to minimize energy waste while still drying laundry effectively. As the technology continues improving, drying cabinets are becoming an increasingly energy-efficient option compared to clothes dryers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drying cabinets can be an energy-efficient alternative to conventional clothes dryers, but they do require some strategic use. The key factors are ensuring the drying cabinet is energy-star certified, not overloading it, cleaning the filter regularly, and running it during off-peak hours. With proper use, drying cabinets consume around half the energy of a vented clothes dryer. They also avoid the heat loss issues of vented dryers. While the upfront cost is higher, over time drying cabinets can provide noticeable savings on energy bills. They also have environmental benefits from reduced energy consumption. However, drying cabinets are best suited to certain climates and households. Overall, they present an eco-friendly drying solution when used correctly.