12 Best Climbing Vegetables That Grow On Vines: Space-Saving Tips
The allure of vine-growing vegetables lies not only in their versatility but also in the unique benefits they bring to the garden. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to maximize space, making them an excellent choice for small gardens or urban agriculture. By utilizing vertical space, these climbers can turn a blank fence or trellis into a lush green wall, adding a touch of natural beauty to any outdoor area.
But it’s not just about aesthetics; vine vegetables are also packed with nutrients and offer a range of health benefits. From the snappy beans to the juicy tomatoes, they’re an excellent source of essential vitamins and minerals. The satisfaction of plucking a fresh cucumber or tomato from your own backyard is unmatched, making it a rewarding experience for gardeners of all levels.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of vine-growing vegetables, exploring their common characteristics, growth habits, and benefits. We’ll also highlight some of the best varieties to grow on vines, including tomatoes, cucumbers, peas, beans, squash, pumpkins, melons, gourds, sweet potatoes, bitter melon, chayote, nasturtiums, and more.
Common Characteristics of Vine Vegetables
Vine Growth Habits
Vine vegetables have a unique ability to ascend upwards, utilizing their flexible stems to grasp onto various surfaces – stakes, trellises, or even adjacent plants. This climbing behavior serves a crucial purpose: it allows them to maximize sunlight exposure, which is akin to a nutrient-rich feast for these veggies. A breakdown of several notable climbers follows: Cucumbers, with their rapid growth rate, require sturdy support in the form of trellises or cages.
Peas, boasting delicate tendrils, thrive under netting or stake-based arrangements. Beans, characterized by their twining vines, benefit from simple stakes or tall poles. Tomatoes, renowned for their robust climbers, necessitate sturdy cages or trellises to support their growth. Melons, featuring heavy-duty vines, demand strong trellis or arbor structures to anchor themselves.
As they ascend, these veggies cleverly avoid soil-borne diseases and pests, leveraging their climbing prowess to remain healthy.
Benefits of Growing Vegetables on Vines
As you begin to cultivate these climbing vegetables, remember that there’s more to the process than simply maximizing space. The benefits extend far beyond just saving room.
Air circulation, for instance, becomes significantly improved when your produce is elevated off the ground. This means a reduced risk of mold and mildew compromising the quality of your food.
Additionally, as these plants reach for the sun, they’re able to absorb more rays, which is akin to a secret ingredient for plant growth. This increased exposure to sunlight strengthens their overall health and enhances their ability to produce flavorful fruits.
But wait, there’s another perk to vertical gardening: it transforms your outdoor space into a visual spectacle.
The lush foliage of these vines can turn an ordinary fence into a thriving green wall, inviting you to step into a hidden oasis.
The advantages of growing vertically are multifaceted:
* Space Efficiency: By training your plants to grow upwards, you can accommodate more in a smaller area – perfect for small yards or balconies.* Healthier Plants: With improved air circulation around the leaves, these crops are less susceptible to disease.
* Ease of Harvest: No longer must you bend and strain to collect your bounty. Your back (and your body) will appreciate this added convenience.* Aesthetic Appeal: Imagine walking into a lush green haven or being surrounded by a verdant curtain – it’s an unbeatable combination.
Growing vegetables on vines is about more than just sustenance; it’s about cultivating a vibrant, visually appealing space that nourishes both body and soul. So why not give vertical gardening a try?
Introduce some vining veggies into your life and watch as your garden – and your meals – undergo a transformation.
Best Vegetables That Grow on Vines
Tomatoes

Beyond the familiar round reds, there’s a world of vine-ripened tomatoes waiting to be discovered. These climbers can grow and produce juicy fruits all season long, offering a unique experience for gardeners. Here are some top picks:
Indeterminate varieties, such as ‘Beefsteak’, ‘Cherry’, and ‘Brandywine’, truly get their vines tangled up in the act of producing tomatoes until the cold weather sets in.
Cherry tomatoes like ‘Sweet Million’ and ‘Sungold’ are fast-growing wonders that produce a constant supply of bite-sized treats. They’re perfect for adding some whimsy to your garden.
Heirloom varieties offer a taste of history, with unique colors and rich flavors like those found in ‘Purple Cherokee’ or ‘Green Zebra’. These varieties are great for creating a stunning vertical garden that’s both beautiful and bountiful.
When it comes to supporting these tomato vines, there are several effective methods. First and foremost, tomatoes are heavy feeders that need solid support to thrive. Here’s how you can keep them happy and upright:
Stakes: A tried-and-true approach is to drive a tall stake next to the plant and tie the stem to it as it grows. This works wonders for keeping your tomatoes off the ground.
Cages: These provide more room for the plant to bush out, allowing it to fill up the cage naturally as it grows. For larger varieties, trellises offer a great option. Train your tomato vines along a trellis for easy access and a stunning garden feature that’s sure to impress. Remember, good support keeps your tomatoes healthy, improves air flow, and makes harvesting a breeze.
Cucumbers

When it comes to growing cucumbers vertically, it’s essential to choose the right type. Cucumbers are like sprinters, quickly producing fruit and spreading out on their trellises. Here’s a breakdown of the best varieties for vertical growth: Slicing cukes like ‘Straight Eight’ are ideal for salads, while pickling types like ‘Boston Pickling’ produce smaller, bumpier fruits perfect for preserving.
English cucumbers, with their slender shape and mild flavor, thrive on trellises and make great additions to sandwiches and wraps. When setting up your vertical cucumber garden, keep in mind that these plants love sunlight – aim for at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. They also require rich, well-drained soil with plenty of compost to promote healthy growth. Consistent moisture is crucial, especially when fruits are forming, so be prepared to water regularly.
Finally, provide support using trellises or nets to keep the fruits straight and prevent them from developing uneven coloration. With these conditions met, cucumbers become a low-maintenance delight that will keep your kitchen stocked with fresh produce all summer long.
Peas

When it comes to growing peas, many gardeners overlook the benefits of vine varieties. But with the right selection, you can reap a bountiful harvest that’s not only delicious but also visually stunning. Here are some top-performing pea varieties that thrive on vines:Snow Peas: These flat, edible pod peas are a staple in many Asian cuisines. ‘Oregon Sugar Pod’ and other robust varieties produce abundantly, making them perfect for snacking or adding to stir-fries.
Snap Peas: Crunchy and sweet, these peas have edible pods that burst with flavor. ‘Sugar Snap’ is a popular choice that vines vigorously, providing a long harvest period. Garden Peas (Shelling Peas): For those who prefer the traditional pea experience, tall varieties like ‘Alderman’ or ‘Telephone’ produce large, sweet peas perfect for shelling and enjoying fresh.
Not only do these varieties climb well, but they also transform your garden trellis into a lush green wall that’s sure to draw attention. To keep your pea vines productive throughout their season, follow these harvesting tips:Regular Picking: The more you pick, the more they produce. Regular harvesting encourages the plant to keep flowering and producing pods, ensuring a steady supply of fresh peas.
Pick Early in the Day: When the pods are firm and crisp, pluck them to reduce stress on the vine and promote healthy growth. Use Two Hands: Hold the vine with one hand and use the other to gently pluck the pod. This helps avoid damaging the plant, keeping it healthy and productive throughout its season. By staying on top of harvesting, you can enjoy a continuous supply of fresh peas over an extended period, maximizing your yield from each plant.
Beans (Pole Beans)
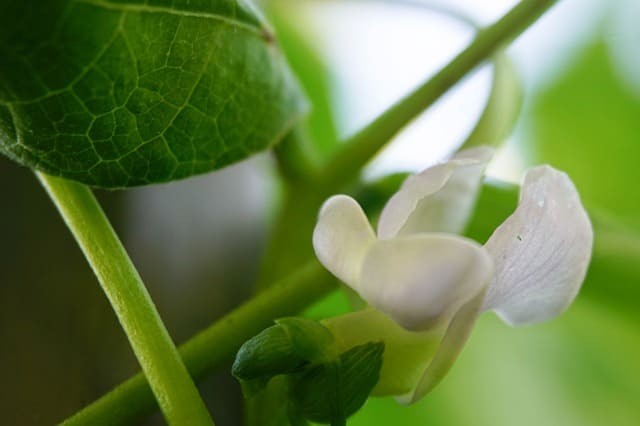

Beans come in two main varieties: pole beans and bush beans. While both types have their own unique characteristics, they differ significantly when it comes to growth habits and requirements.
Pole beans are climbing vines that can reach heights of over 10 feet tall. They require a sturdy trellis or other support structure to grow, and will produce beans throughout the growing season. In contrast, bush beans grow in compact, bush-like forms that typically don’t exceed two feet in height.
These varieties don’t need support and tend to produce all their beans at once, making them ideal for those who want a single, abundant harvest.
Pole beans are particularly well-suited for continuous harvests and vertical gardening, making them perfect for smaller spaces or decorative garden features. They’re also a great choice for gardeners with limited space, as they can be trained to climb up walls, trellises, or other structures.
When it comes to supporting pole beans, the key is to provide sturdy structures that allow the vines to grow and thrive. There are several effective options:
Trellises: A well-made trellis provides a solid base for pole beans to climb, making harvesting easier and more efficient.
Poles: Traditional poles can be used as a simple yet effective way to support bean vines. Bamboo poles or sturdy branches work particularly well.
Netting: Durable garden netting can also be used to support pole beans, providing ample space for the beans to hang and mature.
Providing strong support structures isn’t just important for plant growth – it’s also crucial for keeping your garden tidy and your beans healthy. Watching pole beans climb up and take over their space is a bonus!
Squash (including Zucchini)
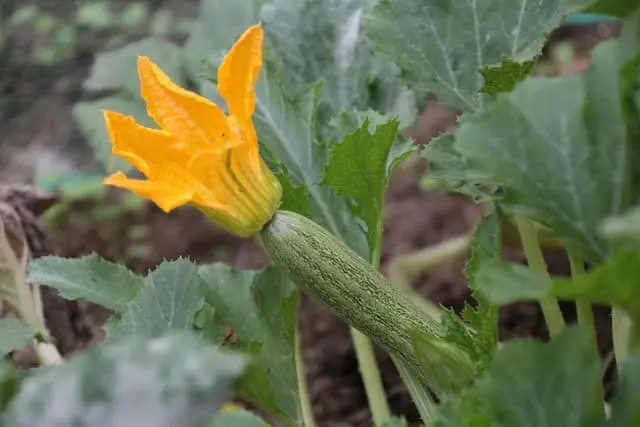

Squash enthusiasts have long prized their versatility in terms of growth habits. While some species thrive as bushy plants, others exhibit vigorous vining tendencies that can be harnessed for vertical cultivation.
The following popular vine-growing squash varieties are well-suited for training up trellises or other supports: Zucchini’s ‘Black Beauty’ and ‘Cocozelle’ are notable examples of this, while Butternut Squash’s ‘Waltham’ variety is particularly renowned for its long, trailing vines that produce exceptionally well in vertical settings. Spaghetti Squash, with its extensive spread, can also be grown vertically to conserve space and prevent fruit rot.
Acorn Squash, often cultivated on the ground, has certain vine varieties that can be trained upwards as well. These versatile options are ideal for adding a new dimension to your garden while still yielding a bountiful harvest. To effectively manage squash vines in small spaces, consider the following strategies: Use vertical structures like trellises or sturdy cages to guide sprawling vines upwards.
Regular pruning of excess growth encourages fruit production and reduces leafy foliage, allowing plants to focus their energy on producing fruits. Choose varieties known for their compact growth habits or those specifically bred for small gardens. Finally, as squash fruits develop, provide additional support using slings or ties to secure heavy fruits to your structure, preventing them from pulling the vine down or breaking.
By mastering these techniques, even the smallest garden spaces can enjoy a productive harvest of delectable squash.
Pumpkins
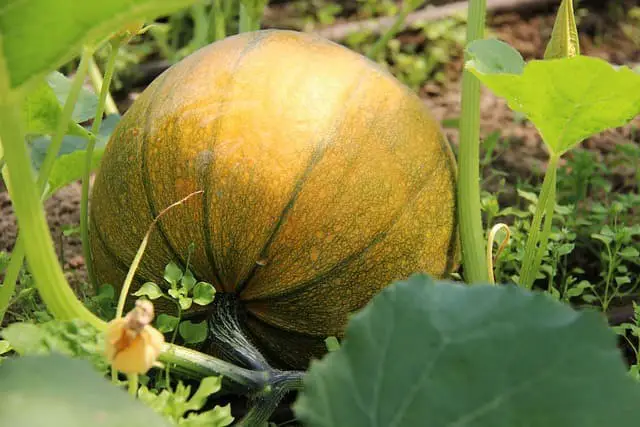

When it comes to choosing the right pumpkin variety for trellising, not all options are created equal. Some smaller varieties are better suited for vertical growth due to their lighter fruit, while others may require additional support to thrive. For example, small sugar pumpkins are a great choice for trellising, as they’re sweeter and can handle being supported vertically.
Jack Be Little and Baby Pam are also excellent options, perfect for adding decorative elements to your garden or using in cooking. To ensure the vines aren’t overwhelmed by the weight of the fruit, it’s essential to select a variety that’s well-suited for trellising. This will prevent stress on the plants and allow them to continue thriving vertically. In addition to selecting the right variety, there are some special considerations to keep in mind when growing pumpkins vertically.
First, make sure your trellises are sturdy enough to support the weight of mature pumpkins. As the fruits grow, they can become quite heavy, so it’s crucial to distribute the weight evenly across the trellis using fabric slings or nets. It’s also important to monitor plant health and adjust your supports as necessary. Keep an eye out for any signs of stress or damage due to the weight of the fruits, and be prepared to make adjustments to ensure the vines continue to thrive.
Growing pumpkins on trellises not only saves space but also reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and can create a visually striking garden feature. With the right varieties and support, vertical pumpkin growing can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience.
Melons (Cantaloupe and Watermelon)
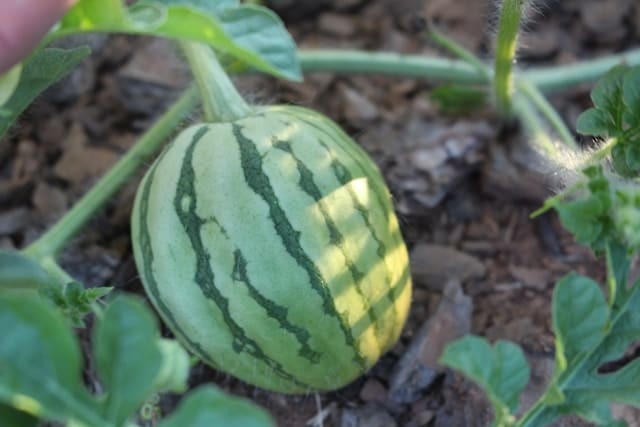

To effectively trellis melons, careful planning is essential due to their size and weight. Start by choosing compact varieties like ‘Sugar Baby’ watermelons or ‘Minnesota Midget’ cantaloupes that are easier to support on trellises.
Select sturdy materials for your trellises, such as wooden frames or thick metal ones capable of holding significant weight. Ensure they’re securely anchored in the ground to withstand the load.
As the vines grow, gently guide them up the trellis using soft ties, distributing the vine’s weight and reducing stress on the plant.
To ensure your melons receive adequate support as they grow, create slings from fabric or mesh to cradle them. This helps distribute their weight evenly, preventing strain on the vines. Regularly inspect the trellis and slings for wear or damage, especially after storms or heavy winds.
Position the slings directly under the melons once they’re large enough to rest in them, adjusting as they grow to ensure continuous support. By providing proper support, you can enjoy the benefits of vertical growing, including improved air circulation around your plants and reduced ground pests.
Gourds
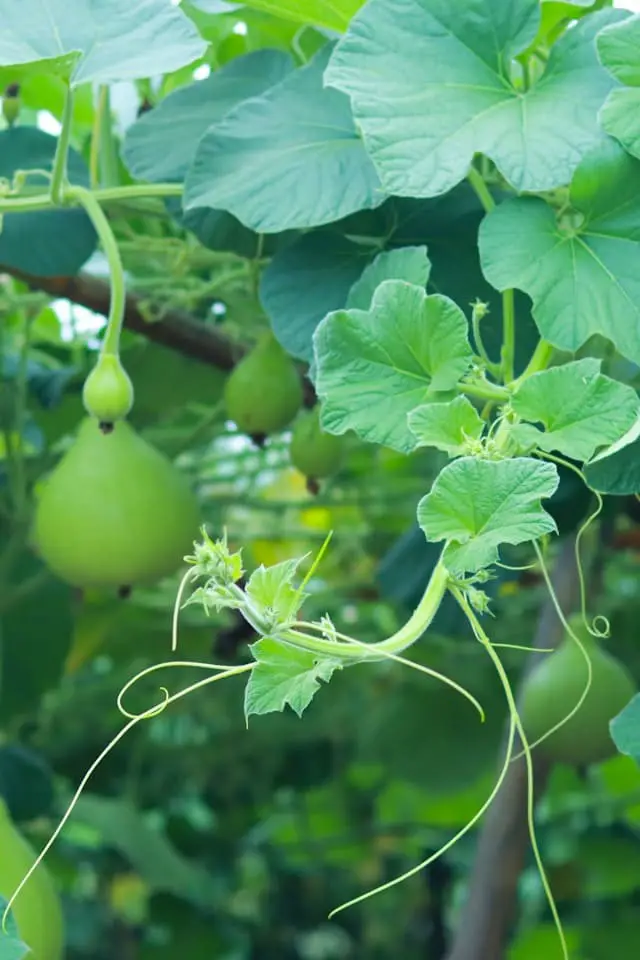

Gourds are a treasure trove of creativity, offering a diverse array of decorative and edible varieties that thrive on vines. From petite, vibrantly colored ornaments to gigantic statement pieces, these versatile fruits provide endless possibilities for artistic expression.
Ornamental gourds like ‘Miniature Bottle Gourd’ and ‘Speckled Swan’ are ideal for crafting unique decorations, while edible varieties such as ‘Bitter Melon’ and ‘Luffa’ offer a flavorful twist on traditional cooking.
‘Giant Bottle Gourd’, for instance, can grow impressively large and is perfect for showcasing artistic talents.
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, gourds also boast a multitude of practical uses. Dried ornamental gourds can be painted, carved, or varnished to create beautiful decorations or holiday ornaments. Larger gourds can be hollowed out, painted, and hung around the garden to add whimsy, while luffa gourds, once dried and processed, make excellent natural sponges for kitchen or bath use.
Growing gourds on vines not only conserves space but also unlocks a world of creative possibilities. Whether you’re looking to elevate your cooking, home decor, or garden art, these fascinating fruits are sure to inspire.
Sweet Potatoes

Sweet potatoes are often associated with sprawling growth, but with clever techniques, they can thrive in vertical gardens. To make the most of your space, consider using tower gardens or vertical planter boxes where the vines can cascade over the edges and tubers develop within the confined space. Training the vines upward using trellises or stakes is also effective, allowing for easier harvesting and maximized garden space.
To ensure optimal growth, sweet potatoes require specific soil and water conditions. They flourish in well-drained, sandy soil with a slightly acidic pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Consistent moisture is crucial, with regular even watering especially during the peak growing months of summer. By paying attention to these needs, vertical gardeners can successfully cultivate sweet potatoes, making them a rewarding crop for maximizing space.
Bitter Melon
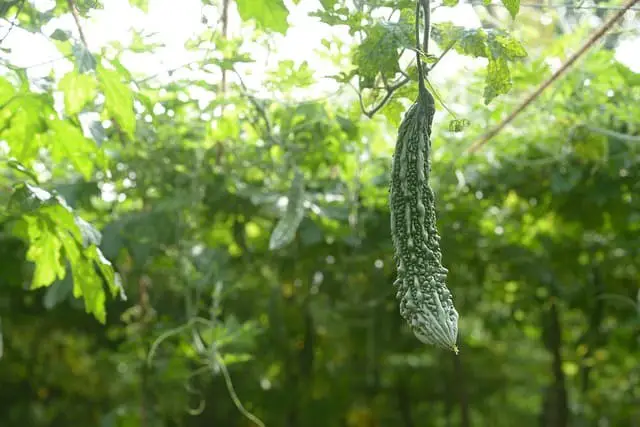

Bitter melon is deeply ingrained in various Asian and African cuisines, where it’s cherished for its bold flavor and impressive medicinal properties. This remarkable fruit is not only a staple ingredient but also a celebrated component of cultural festivals, highlighting its numerous health benefits.
Its unique characteristics have earned bitter melon a special place in traditional dishes, where it’s often used to regulate blood sugar levels and promote digestive well-being.
Additionally, this superfruit is rich in essential vitamins like C and A, as well as vital minerals such as iron and potassium.
For gardeners looking to successfully cultivate and harvest bitter melon, understanding its specific requirements is crucial. This requires a warm, humid environment with full sun for most of the day. Providing sturdy trellising is also essential, as the vines can grow quite long.
Harvesting the fruit when it’s still green and firm ensures the best flavor and texture; however, be aware that the fruit turns yellow and becomes too bitter as it matures.
Chayote
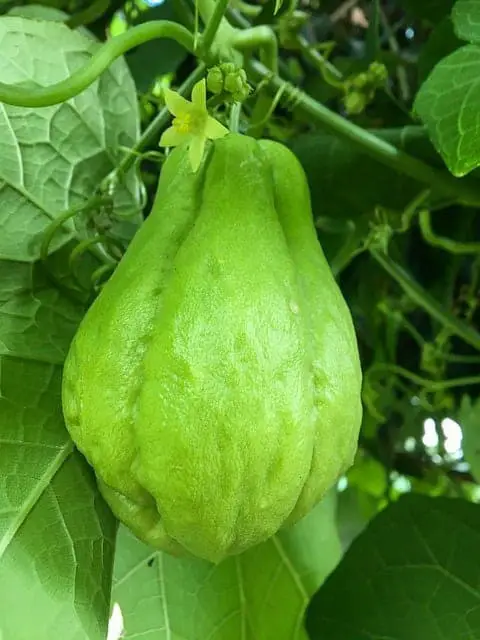

To cultivate thriving chayote plants, it’s essential to understand their specific climate and support requirements. Chayotes prefer warm temperatures between 50-80°F (10-27°C), making them sensitive to frost. When growing in areas prone to freezing temperatures, it’s crucial to provide protection or wait for a frost-free period.
To accommodate the heavy vines of chayote, robust support systems are necessary.
Trellising is an effective method, where sturdy trellises can bear the weight of the vines and developing fruit. Adequate spacing between plants (around 10 feet) ensures the trellis has sufficient room to accommodate the vine’s growth.
Regular maintenance is also crucial, as trellises may need to be checked and reinforced throughout the season to ensure they can support the vines’ weight.
By providing proper support and climatic conditions, chayote plants will remain productive and healthy, yielding a bountiful harvest.
Nasturtiums (Edible Flowers)
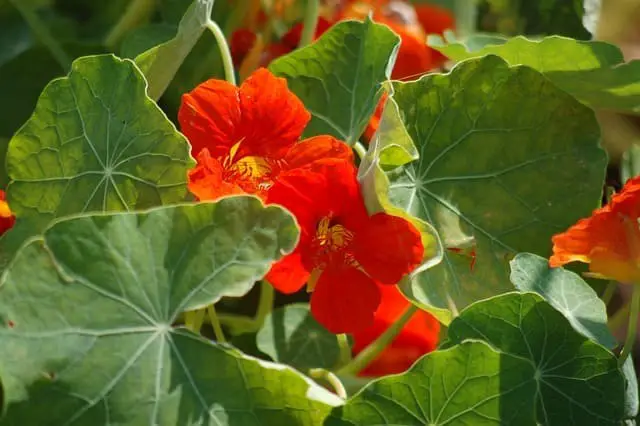

Nasturtiums are a versatile addition to any vegetable garden, offering not only their stunning visuals but also edible leaves and flowers. By incorporating these plants into your garden, you can reap several benefits. One way to utilize nasturtiums is through interplanting. Simply scatter the seeds among your vegetables, allowing the bright flowers to attract beneficial pollinators like bees and butterflies.
This is particularly useful for crops that rely heavily on these insects, such as tomatoes and cucumbers. Alternatively, you can use nasturtiums as a natural border around your garden beds. Not only will this add a pop of color, but it will also serve as a trap crop for pests, drawing them away from your more valuable vegetables. For those with limited space, consider training nasturtiums to grow vertically on small trellises or along fence lines.
This will allow the plants to cascade beautifully, creating a charming display that’s hard to ignore. When used as companion plants, nasturtiums offer several advantages. They are known to repel a variety of pests, including aphids and cucumber beetles, which can be detrimental to vegetable crops. Additionally, their deep taproots help to break up compacted soil and improve overall soil health. But perhaps the most significant benefit is the attraction of beneficial insects.
The vibrant flowers not only draw in pollinators but also beneficial insects that prey on common garden pests, helping to maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Growing Tips and Care for Vine Vegetables
Soil Preparation and Fertility Needs
When it comes to growing vine vegetables, having good soil is crucial. These climbers have specific requirements when it comes to their root system. To get started, you’ll want to focus on creating a well-draining environment that’s free from waterlogged areas. If your garden bed tends to retain too much moisture, consider elevating the beds or incorporating organic matter to improve drainage.
Next, you’ll want to provide your vine veggies with a nutrient-rich environment.
These plants are heavy feeders and will thrive when given a boost of compost or aged manure. A balanced, slow-release fertilizer can also be beneficial, but be cautious not to overdo it – too much fertilizer can result in an abundance of leaves rather than vegetables.
Finally, pH levels play a significant role in the success of your vine vegetable garden. Most varieties prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.0-7.0.
Testing your soil’s pH and making adjustments as needed using lime or sulfur is relatively straightforward.
Watering Requirements and Techniques for Vertical Growing
When it comes to watering plants that are growing upwards, timing and technique become crucial factors. It’s not just about the amount of water you provide, but also when and how you deliver it.
For vine vegetables, consistency is essential. A steady supply of water helps them thrive. Drip irrigation is particularly effective because it targets the roots directly, minimizing evaporation and reducing the risk of diseases by keeping leaves dry.
To take it a step further, consider applying an organic mulch around your plants. This not only reduces surface evaporation but also keeps the soil moist on hot days, allowing those roots to stay hydrated.
Ultimately, monitoring weather patterns and soil moisture is crucial to avoid over- or under-watering. Check the soil with your finger – if it’s dry an inch below the surface, it’s time to give it some TLC.
Common Pests and Diseases and How to Manage Them
In the world of gardening, few things can be as frustrating as dealing with pests and diseases that seem to appear out of nowhere. But fear not, for with a little vigilance and some smart strategies, you can keep your garden thriving.
The key is to stay on top of potential problems from the start. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of trouble – whether it’s wilting leaves, suspicious spots, or stunted growth. The sooner you catch issues, the easier they are to manage.
Another effective way to keep pests at bay is to cultivate a diverse community of beneficial insects in your garden. Ladybugs, spiders, and praying mantises are all valuable allies that can help keep unwanted visitors under control.
Preventing disease is also crucial. By avoiding overhead watering and instead opting for soaker hoses or gentle showers, you can keep your plants’ foliage dry and reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
Additionally, practices like crop rotation and proper spacing can go a long way in preventing many problems by reducing the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying a bountiful harvest from your garden. With balance, attention, and a little know-how, you can overcome even the most pesky of pests and diseases, and reap the rewards of a thriving and productive garden.
Harvesting and Using Vine-Grown Vegetables
Tips on When and How to Harvest for Best Flavor and Yield
To harvest your vine-grown vegetables at the right time, it’s essential to develop a sense of intuition and observation. Each vegetable has its unique characteristics that signal readiness for picking. For instance, tomatoes typically turn a deep, even color, while cucumbers feel firm and have a glossy skin when ripe. Peas are best picked when their pods are plump and easily snap in half.
When it comes to timing, aim for early morning harvests when the air is still cool and the vegetables are at their freshest. The afternoon sun can cause flavors to fade quickly, so it’s crucial to strike while the iron’s hot, as it were. Using the right tools is also vital to avoid damaging the plant’s structure. A pair of garden shears or a sharp knife will allow you to snip fruits from the vine without yanking on them. A clean cut can help prevent diseases and promote healthy growth.
By harvesting your vegetables regularly and carefully, you’ll encourage more produce throughout the season. This means more opportunities for fresh salads, hearty stews, and of course, those delightful snacks straight off the vine.
Ideas for Using Vine-Grown Vegetables in Recipes
Transform your bountiful harvest into mouthwatering meals with these simple and delicious ideas:
Stir-Fries and Salads: Elevate any dish with the freshness of cucumbers, snap peas, squash, or tomatoes. Simply slice them up and toss them in with your favorite dressing or sauce for a burst of flavor.
Grilling and Roasting: Bring out the natural sweetness in vegetables like tomatoes, squash, and cucumbers by grilling or roasting them.
Brush them with olive oil, sprinkle some salt, and let the heat do its magic.
Pickling and Preserving: Don’t rush to devour everything at once! Preserve your harvest through pickling or making a batch of tomato sauce. These methods not only capture the essence of summer but also provide a stash of tasty treats for the colder months.
Conclusion
Growing vines in your vegetable garden is a clever way to maximize space while adding a touch of elegance and whimsy. Not only do these climbers create a sense of airiness by circulating the air, reducing the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, but they also provide effortless sunlight exposure, leading to healthier and more abundant harvests.
The lush tendrils of peas, the cascading pumpkins, or even the delicate sprouts of cucumbers all contribute to a visually appealing and functional garden. Whether you’re working with a spacious backyard or a compact balcony, there’s a vine vegetable that can flourish in your unique environment. Start small with tomatoes or cucumbers and bask in the satisfaction of plucking fresh vegetables from your own vertical haven.
It’s not just about the harvest; it’s about transforming your outdoor space into a vibrant, thriving extension of your home.
Frequently Asked Questions About Growing Vegetables on Vines
What are the best vegetables to grow on vines for beginners?
When embarking on a vine gardening journey, beginners often find success with tomato and cucumber cultivation. These versatile plants are forgiving, requiring only basic trellis support, and can yield an abundance of fruit when provided with optimal growing conditions. The ease of care and rapid returns make them ideal entry points for new enthusiasts.
How much space do I need to grow vine vegetables?
When it comes to growing vine vegetables, the key to success lies not in the size of your outdoor space, but rather in how you utilize it. By incorporating vertical gardening techniques, even the smallest balconies and patios can become productive plots for vine veggies. Trellises, stakes, and vertical planters are just a few tools that can help you train your vines to grow upwards, maximizing your available space while minimizing the footprint of your plants.
Do vine vegetables require special soil conditions?
For optimal growth, most vine varieties favor a well-draining soil profile that’s rich in organic matter. A slightly acidic to neutral pH also tends to suit them well. By incorporating compost or a balanced fertilizer into your gardening routine, you can foster healthy plant development and ultimately enjoy bountiful harvests.
How often should I water vine vegetables?
When it comes to watering vine vegetables, consistency is key. Aim to keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, particularly during periods of drought. A reliable way to achieve this is by utilizing drip irrigation systems or soaker hoses, which deliver steady moisture directly to the roots while keeping the foliage dry and free from excess moisture. This approach ensures that your vine vegetables receive the right amount of hydration without compromising their overall health.
What common pests and diseases should I watch out for with vine vegetables?
While cultivating a lush and thriving garden, it’s essential to be mindful of the common pests that can wreak havoc on your plants. Aphids, cucumber beetles, and vine borers are just a few examples of the unwanted visitors that can damage your crops. Furthermore, diseases such as powdery mildew and blight can also pose significant threats to your garden’s health. To mitigate these issues, regular inspections of your plants become crucial, allowing you to catch any problems early on.
Proper spacing between plants and encouraging air circulation through thoughtful planting layouts can also help reduce the risk of infestation or disease spread. Another effective strategy is crop rotation, which helps break the life cycle of many pests and diseases. For a more natural approach, consider using organic pesticides or attracting beneficial insects to your garden.
By incorporating these tactics into your gardening routine, you’ll be well on your way to cultivating a robust and resilient garden.