What Is Rubber Rolls?
What are Rubber Rolls?
Rubber rolls are large sheets of rubber material that are rolled out in sections to create flooring. They are a popular choice for gymnasiums, weight rooms, playgrounds, and other athletic facilities due to their durability and shock-absorbing properties.
Rubber rolls are available in a variety of thicknesses, textures, and colors. The rolls come in different widths, typically ranging from 4 to 6 feet wide. Standard roll lengths are generally 30 to 40 feet. By laying rolls side-by-side and adhering them together, rubber rolls can cover large open spaces seamlessly.
The primary material used to manufacture rubber rolls is vulcanized recycled rubber. The rubber granules are heated and bound together using adhesives to create a strong, resilient rubber sheet. The rolls provide cushioning and impact absorption, making them well-suited for sports and recreational flooring applications.
Compared to loose rubber tiles, rubber rolls offer a more seamless appearance and enable faster installation times. The rolls create an even, consistent flooring surface since there are fewer seams between pieces. Overall, rubber rolls provide a heavy-duty, durable rubber flooring solution for various commercial and athletic facilities.
Types of Rubber Rolls
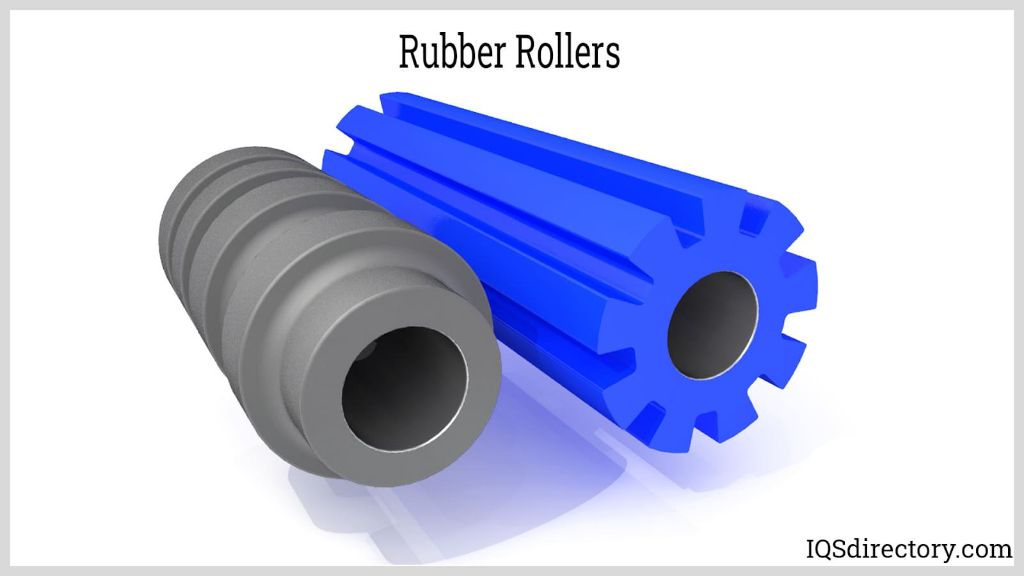

There are several common types of rubber rolls used in various industrial applications:
Feed Rolls
Feed rolls are used to feed material into a machine at a consistent rate. They have a friction surface to grip the material and rotate to pull it through the process. Feed rolls are commonly used in printing, textiles, paper mills, and other continuous processes. Different rubber covers like neoprene and silicone provide the right grip and friction for the material. Common types of rubber feed rolls include sand blasted and machined rollers. They often include grooves or indentations to improve grip on the material. High release rubber rolls like silicone are used when adhesion needs to be minimized (Industrial Rubber Rollers).
Pressure Rolls
Pressure rolls apply force and pressure to material passing through. This may compress, smooth, or flatten the material during manufacturing. Pressure rolls come in various levels of hardness to provide the right amount of pressure for the application. Harder rubber covers like neoprene and polyurethane are frequently used. Pressure rolls assist processes like calendering, laminating, coating, embossing, and printing. They are commonly paired as top and bottom rolls to exert force from both sides (Rubber Roller: What Is It? How Is It Made? Types, Uses). Some types have a center-crowning design to distribute force evenly along the roll face.
Guide Rolls
Guide rolls, also called idler rolls, control web tension and guide the material through the production line. They prevent sagging and wrinkles by keeping optimal tension as the material is processed. Ball bearing guide rolls allow high speed operation. Various cover materials like neoprene provide grip while minimizing damage to delicate materials. Some common types are crowned rolls, bowed rolls, and tapered rolls for specialized tension control (12 Common Types of Rubber Rollers).
Rubber Roll Materials
Rubber rolls are available in a wide range of rubber compounds to suit different applications and operating conditions. Some of the most commonly used rubber materials for rolls include:
Silicone rubber: Silicone rubber offers excellent heat resistance and low compression set. It maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range of -55°C to 250°C. Silicone rolls resist weathering and ozone, have good chemical resistance, and provide excellent release properties. Common applications include heat rolls, driving rolls, and paper machine press rolls. Source
EPDM rubber: EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber has excellent ozone, weathering and aging resistance. It has good chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, ketones, and phosphates. EPDM retains flexibility at low temperatures down to -45°C. It is often used for coverings and linings in the chemical, automotive and construction industries. Source
Natural rubber: Natural rubber offers high tensile strength, resilience, abrasion and tear resistance. It provides good dynamic properties and fatigue resistance. Applications include drive rolls, transport rolls, and calender rolls for paper, textiles, plastics and metals. It is not suitable for oil resistance. Source
Rubber Roll Manufacturing Process
There are three main processes used to manufacture rubber rolls:
Extrusion
Extrusion involves pushing rubber compound through a die to create a continuous shape with a fixed cross-section. This allows rubber rolls to be produced in long lengths that can later be cut to size. The rubber is first fed into an extruder barrel and conveyed forward by a rotating screw. As the rubber moves through the barrel, heat and pressure turn the compound into a molten mass. The molten rubber is then forced through the shaping die at the end of the barrel, producing an extruded profile with the desired shape and dimensions (https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/rubber-roller.html).
Rubber Injection Molding
With injection molding, uncured rubber is injected into a mold cavity and cured under heat and pressure. This produces rubber parts that hold tighter tolerances than extrusion. The rubber is heated until it becomes fluid and is then injected under pressure into a two-part mold. The mold is kept cool so the rubber solidifies quickly into the desired shape. Once cured, the part is removed from the mold (https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/rubber-roller.html).
Calendering
Calendering uses a series of rollers to form continuous sheets of rubber compound. The rubber is fed between rotating heated metal rolls and is squeezed into sheets of a specified thickness. By adjusting the gap between rolls, the calendering process can produce sheets of various thicknesses. The rubber sheets can then be cut to size for rubber rolls or other rubber parts (https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/rubber-roller.html).
Rubber Roll Properties
Some of the key properties of rubber rolls are their durometer, elasticity and resistance. Rubber rolls have a wide range of durometer or hardness ratings, with softer rolls rated around 50A and harder industrial rubber rolls rated up to 90A. The flexibility or modulus of a rubber roll impacts how much it will compress under load. Softer, more elastic rubber rolls are better for conforming to surfaces and absorbing vibration. Harder rubber rolls with lower elasticity are more rigid and durable.
Rubber rolls have good abrasion and tear resistance compared to other elastomers. Nitrile rubber offers excellent wear resistance and resilience. The chemical resistance of rubber rolls depends on the material, with viton and silicone generally having the best resistance to oils and solvents. Proper material selection ensures the rolls will retain their properties when exposed to chemicals in the application environment.
Rubber Roll Applications
Rubber rolls are used in a variety of industrial applications due to their durability, flexibility, and friction properties. Some of the most common applications include:
Paper Industry
In the paper industry, rubber rolls are used on paper machines and in paper coating processes. Press rolls apply pressure to squeeze water out of the paper web and to press the paper against dryer cylinders. Rubber covered calender rolls are used to smooth and glaze the surface of paper. Coating rolls apply sizing and coating solutions evenly across the paper surface.[1]
Printing
Rubber inking rollers transfer ink from ink fountain rollers to printing plates in offset printing presses. The rubber allows for consistent ink transfer and helps prevent issues like hickeys. Rubber blanket cylinders transfer the inked image to the substrate being printed.[2]
Textiles
Rubber covered rolls are used in textile manufacturing for processes like dyeing, drying, printing, and finishing. The rolls guide and feed the fabric through the machinery without damaging it. Rubber allows the rolls to grip the material properly.[3]
Metals
In metal rolling mills, work rolls often have a rubber covering. The friction and cushioning provided by the rubber allows the mill to grip and reduce metals into thinner sheets or strips without scratching the surface.[1]
[1] https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/rubber-roller.html
[2] http://www.industrialrubbergoods.com/industrial-rubber-rollers.html
[3] https://vintexrollers.com/know-the-various-kinds-of-rubber-rollers-for-best-uses/
Advantages of Rubber Rolls
Rubber rolls offer several key advantages that make them a popular flooring choice in many applications:
Grip and Friction – The textured surface of rubber rolls provides excellent grip and friction, making them ideal for use in gyms, weight rooms, and other athletic settings where traction is important. The high friction helps prevent slips and falls on rubber roll flooring (source).
Flexibility – Rubber rolls are very flexible and able to conform to uneven subfloors. This flexibility allows the rubber to absorb impacts rather than transfer force, helping prevent injuries during activities like weightlifting or gymnastics (source).
Vibration Dampening – The elastic nature of rubber rolls helps dampen vibrations and sound. This makes them useful for insulating against noise and reducing echo in gyms, exercise rooms, and industrial settings.
Disadvantages of Rubber Rolls
Some key drawbacks and disadvantages to consider with rubber rolls include:
Wear and Tear: Over time and heavy use, rubber rolls will show signs of wear and tear through scuffing, scratching, indentations, and compression. This can lead to an unsightly appearance and potentially unsafe flooring [1]. Proper maintenance and rotation or replacement of high traffic sections can help prolong the life of rubber rolls.
Damage Vulnerability: While highly durable, rubber rolls can be susceptible to damage from sharp objects or improper use of equipment. Rolls used in gyms or playrooms may develop tears and rips over time [2]. Proper care is required to prevent avoidable damage.
Maintenance Requirements: Rubber rolls require regular maintenance such as sweeping and damp mopping to keep clean. Harsher chemicals and abrasives cannot be used for cleaning. Sections may need to be repaired or replaced over time to maintain safety and aesthetics [3]. Proper maintenance must be kept up.
Rubber Roll Maintenance
Proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of rubber rolls. Here are some key maintenance tips:
For cleaning, a mild detergent or neutral pH cleaner diluted with warm water is typically recommended. Avoid harsh chemicals that could degrade the rubber. Gently scrub the surface with a soft brush or scrubbing pad. Rinse thoroughly with clean water and allow to fully dry (source).
Rubber rolls should be stored clean and dry. Exposure to light, ozone, and extreme temperatures can cause premature aging. Storing rolls vertically on end will help maintain their shape (source).
For roller applications, clean the rubber surface regularly with isopropyl alcohol to remove ink buildup and debris. Check for cracks, chips or significant wear. Replace rollers when rubber hardens or performance declines (source).
Consult the manufacturer’s care guidelines for any product-specific maintenance recommendations. Proper cleaning and storage will maximize rubber roll lifespan.
Notable Rubber Roll Manufacturers
There are several leading and notable companies that manufacture rubber rolls. Some of the top rubber roll manufacturers include:
American Urethane – American Urethane is one of the top rubber roller manufacturers in North America. They specialize in manufacturing urethane, rubber and specialty rollers for industrial applications. The company utilizes innovative polymer technologies to create high performance rollers.
Harwood Rubber Products – Founded in 1937, Harwood Rubber is one of the oldest and most trusted rubber roller manufacturers. They offer a full range of molded rubber and polyurethane rollers for various industries. The company has state-of-the-art facilities in Wisconsin.
REDCO – REDCO specializes in engineering and manufacturing high quality rubber, polyurethane, and silicone rollers. They utilize innovative designs and compounds to create rollers that provide optimal performance in demanding industrial applications.
Other leading rubber roll manufacturers include Weaver Industries, Urethane Source, and Advance Rubber. When selecting a rubber roll manufacturer, key factors include industry experience, engineering expertise, innovative technology, and high quality standards.